Fuel Cell
Fuel Cell

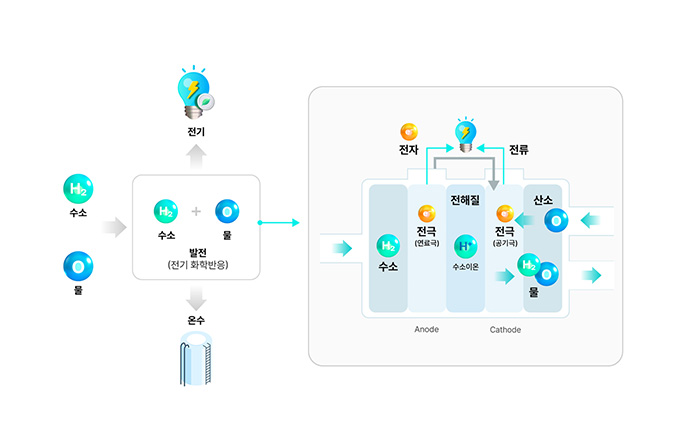
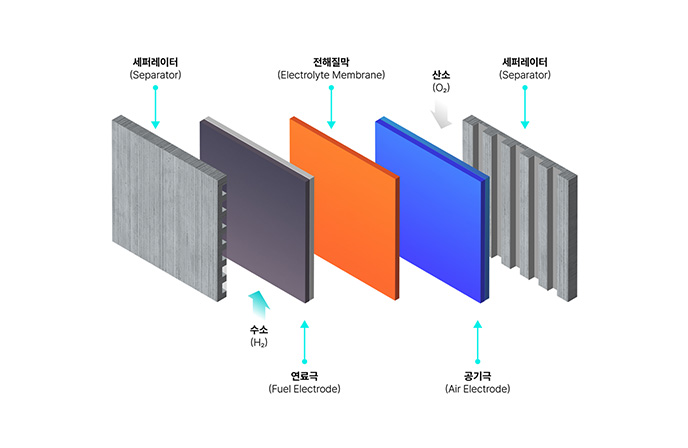
Fuel Cell Power Generation System
Utilizing Fuel Cells in Mobility
-
 Vehicle Applications
Vehicle Applications
Due to fast charging times and long driving ranges, fuel cells are particularly suitable for medium and long-distance travel.
-
 Medium to Long-Distance Commercial Vehicles
Medium to Long-Distance Commercial Vehicles
Applicable to commercial vehicles such as trucks, buses, and trains that operate over long distances. The high energy density and quick charging time of hydrogen fuel cells are advantageous for long-distance travel and transporting heavy cargo.
-
 Industrial Use
Industrial Use
Can serve as an emergency power supply in places like hospitals, data centers, and factories. Additionally, they can be utilized as transport vehicles within warehouses or manufacturing facilities.
-
 Aviation and Maritime Transport, Equipment
Aviation and Maritime Transport, Equipment
Not only applicable to aviation and maritime transport vehicles like ships, but can also be employed in fields such as monitoring sea pollution, accidents, and illegal fishing.