Fuel Cell
A fuel cell is a technology that produces electricity and heat simultaneously through the electrochemical reaction between hydrogen and oxygen in the air. It is an innovative device with a power generation efficiency of 30-40%, thermal efficiency of over 40%, resulting in an overall efficiency of 70-80%. As it is free from pollution and noise, it can be utilized in various fields, ranging from small-scale mobility to large-scale power generation. Alongside hydrogen energy, it is gaining attention as a future energy device.

Utilizing Fuel Cells in Drones
The use of fuel cell technology in drones addresses energy supply issues, providing solutions for long-distance flights,
extended flight times, and increased flexibility. Drones powered by fuel cells find applications in various sectors such as military,
commercial, agriculture, environmental exploration, and more. As drone technology and fuel cell advancements progress,
it is anticipated that they will be employed in even more diverse fields in the future.
- Long Flight Times
Drones operate using batteries, and the limited battery capacity restricts the flight time. However, utilizing fuel cells provides higher energy density, enabling extended flight durations with just one fuel charge.
- Energy Efficiency
Fuel cells directly convert chemical energy into electrical energy, offering higher energy efficiency than batteries. This allows drones to move faster, more efficiently, and cover longer distances.
- Quick Charging Time
Fuel cells can be rapidly charged, minimizing downtime and allowing drones to operate swiftly.
- Weight Reduction and Performance Improvement
Fuel cells can be made smaller and lighter than batteries, providing high output and performance. This enhances the payload capacity and stability of drones.
- Sustainability and Environmental Friendliness
Fuel cells use hydrogen and oxygen as fuel, producing no emissions, making them environmentally friendly and sustainable energy sources.
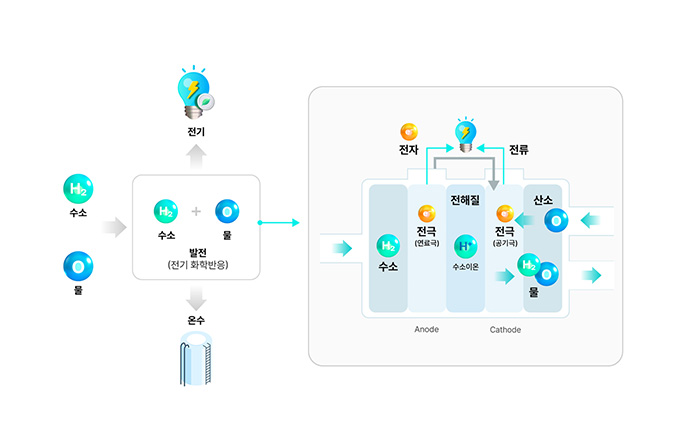
- Hydrogen flowing into the fuel electrode undergoes oxidation by platinum catalyst, breaking down into hydrogen ions and electrons.
- Hydrogen ions generated at the fuel electrode move through the electrolyte membrane to the air electrode, while electrons travel through an external circuit to the air electrode.
- Hydrogen ions and electrons reaching the air electrode combine with oxygen to produce water.
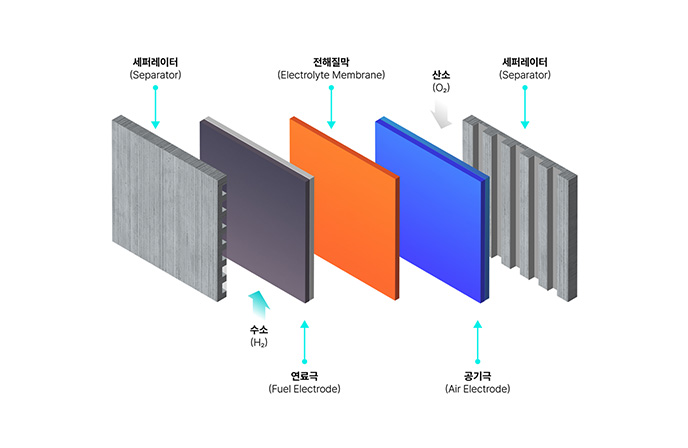
- The stack is the core component of a fuel cell, comparable to the engine in gasoline power generation.
- It is composed of multiple unit cells arranged in series. The generated current is proportional to the cell area, and the voltage is proportional to the number of cells stacked.
- Each cell consists of a Membrane-Electrode Assembly (MEA), Gas Diffusion Layer (GDL), and separator plate.
